Master's Project
Students can find on this page the general requirements and evaluation system for a Master's Project at the Chairs of Urban Water Management at ETH Zurich. They can also find a list of currently offered topics.
Supervisors can find on this page information about the requirements the students must fulfil to complete a Master's Project at the Chairs of Urban Water Management at ETH Zurich, organizational and didactical information and the templates for the proposal of new Master's Projects.
Information for Students
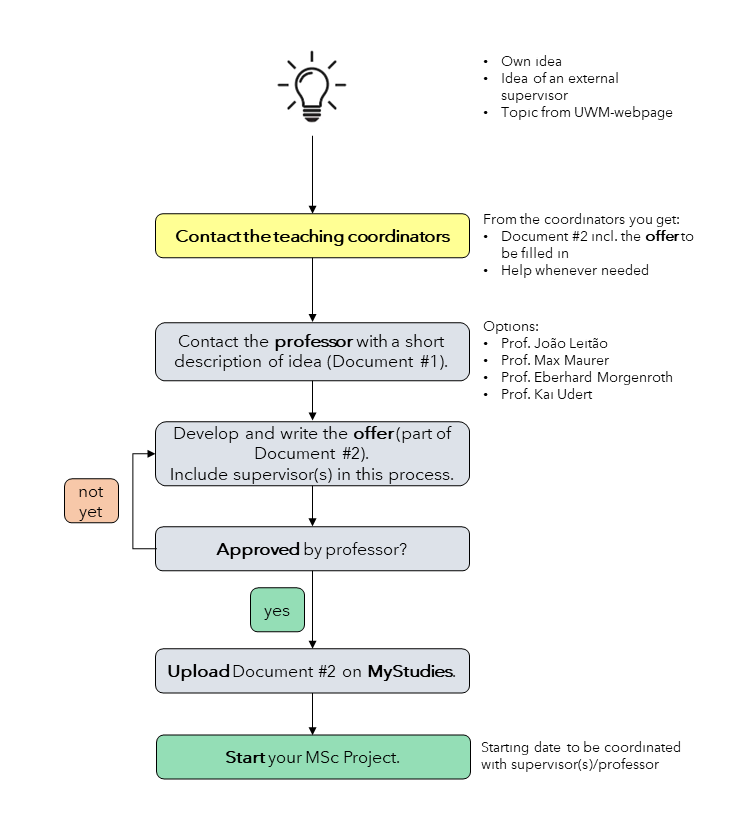
Would you like to start a Master's Project Work with the Chairs of Urban Water Management? The schematic provides an overview of the necessary steps. Please read the Guidance PDFs below. Communicate your intention to the responsible teaching coordinator and contact them for any additional information.
- Download Guidance MSc Project at SWW (PDF, 142 KB)
- Download Guidance for BSc and MSc Theses and Projects in Environmental Engineering (PDF, 160 KB)
- Download Guidance MSc Project in Environmental Engineering (PDF, 197 KB)
- Download Citation-Guidelines (PDF, 65 KB)
- Download Guide to report writing (PDF, 68 KB)
- Download Evaluation criteria (PDF, 64 KB)
- Plagiarism
- Prevention of plagiarism
Information for Supervisors
Would you like to supervise a thesis for the Chairs of Urban Water Management? Please read the Guidance PDFs below and use the Project Work Proposal Template to submit a topic to the responsible teaching coordinator. A professor will have to approve the topic before it will be uploaded on this page.
To promote your topic further, you are welcome to send us a short slide deck about your proposed topic(s). Our professors can then publicize your thesis topic during their lectures.
Contact
For inquiries or to submit a proposal, please check the Teaching Coordinators webpage and contact the coordinator responsible for Master's Projects.
Currently Offered Topics
Below you can see the topics currently offered by EAWAG researchers and private partners. If you are interested in one of the offered topics, contact the person indicated. Once you agree you will do your Master's Project with them, contact the responsible teaching coordinator to obtain the documentation form.
You can also independently find a supervisor to develop your own topic. In this case, inform the responsible teaching coordinator from the beginning and a potential supervising professor of your intention. Be aware that the professor will have to approve a certain topic as the subject of a Master's Project.
The HIL building at ETH will undergo a substantial renovation. ETH aims to create a showcase how cutting-edge technologies can make buildings more sustainable. With this master project we would like to develop a water concept that fits this inspiration... Read More

The municipality of Würenlos is currently planning the construction of a new drinking water reservoir. This raises the question of how the old reservoir could be repurposed to make a positive contribution to sustainable urban water management. The main goal of the municipality is to reduce the overall drinking water extraction from their groundwater resources. The aim of this project is to conduct a feasibility study to identify and evaluate 2-3 potential reuse options for the old reservoir. In the next phase, the best option will be selected and dimensioned. The project ... Download Read More (PDF, 203 KB)

Water scarcity is a threat to agricultural activities, even in Switzerland. For this reason, reduced water consumption and the reuse of treated water for household and irrigation purposes are becoming increasingly attractive. However, when reusing water, it must be ensured that the treated water does not pose any health or environmental risks. As part of this master's project, you will scientifically supervise a greywater reuse system by monitoring whether the system meets legal requirements. In September 2024, a system will be put into operation on a permaculture farm in the canton of Lucerne, designed to close the water cycle of the residential building. The farm ... Download Read More (PDF, 115 KB)

Many municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) around the world are approaching their maximum capacities, while the space is limited for plant expansion or new facilities. With increasingly stringent legislative requirements, there is a crucial need of biological process intensification. Densified Activated Sludge (DAS), a mixture of flocs and small, dense granules (average diameter ca. 200~500 microns), offers significant advantages over conventional activated sludge, such as higher biomass retention and improved settleability [1, 2]. Several Swiss WWTPs, including the biggest WWTP in Zurich “Werdhölzli”, are adopting DAS to enhance treatment efficiency ... Read MoreDownload (PDF, 673 KB)
Contact: Mengqi Zhu ()
In Switzerland, sewer networks are the most expensive infrastructure of municipalities and cities. Sewer networks are designed to fail once in 5 to 20 years. This means that proper design and operation fundamentally depends on adequate rainfall information. In this thesis, available rainfall generators will be applied to produce synthetic rainfall series for the entire CH, based on available rainfall information from MeteoSwiss, e.g. from rain gauges, weather radar and statistical analysis and other sources. It will thus basically improve ... Download Read more (PDF, 297 KB)
Contact: Lauren Cook ()
Nitrite accumulation is a common problem in wastewater treatment, especially in sequencing batch reactors (SBR) and in the treatment of high-strength wastewater such as digester supernatant or urine. A novel amperometric sensor has been successfully applied for measuring and controlling nitrite build-up in urine treatment. In this master's project, the student or students shall determine whether the sensor can also be used for nitrite measurement and control in SBRs or other activated sludge systems operated with municipal wastewater treatment.
The objective of this project is... Download Read more (PDF, 123 KB)
Swiss wastewater treatment plants may require nitrogen removal efficiencies of 70-80% or more in the future. This poses a significant challenge for denitrification in the biological treatment processes of many WWTPs. Capacity expansions, retrofitting, and operational optimizations will be necessary in many cases. In this master project, a case study... (Download Read more (PDF, 68 KB))
Contact: Alain Meyer ()
This work is part of an effort to optimize a novel treatment technology that reduces the nitrogen load of N-enriched side-streamt from municpal wastewater plants and produces a valuable fertilizer. Improvements in specific steps of the process can be made to facilitate continuous operation and reduce the capital and operational costs. This work will look deepeter into chemical processes occurring during the pretreatment step ... Download Read more (PDF, 174 KB)
Contact: Christophe Bonvin ()

Die ARA Altenrhein möchte die diversen Themen der Abwasserreinigung (Energie, Lachgas, Stickstoffelimination, Kreislaufwirtschaft) meistern. Altersbedingt müssen diverse Einrichtungen der Belebtschlammbiologie ersetzt werden. Für die Steigerung der Stickstoffelimination soll die Biologie zusätzlich kaskadiert werden. Das Ziel der Arbeit ist der Aufbau und die Kalibrierung eines Modells für die ARA Altenrhein in SIMBA#... (Download Read more (PDF, 251 KB))
Contact: Tobias Bührer ()

Der energieintensivste Posten auf einer ARA ist die Belüftung, welche von der CSB-Fracht im Zulauf abhängig ist. Mehr als 50–60 % der CSB-Gewässeremissionen in Einzugsgebieten mit Mischwasserkanalisation stammen aus Entlastungsbauwerken. Im Einzugsgebiet zur ARA Bachwis befindet sich ein Entlastungsbauwerk, welches Mischwasser in den Greifensee entlastet. Im Rahmen der Arbeit soll die Polstofffiltration auf ihre Eignung als Rohwasserfiltration getestet werden (erhöhte CSB-Ausschleusung, Ersatz/Entlastung Vorklärung)... (Download Read more (PDF, 134 KB))
Contact: Nikolai Otto ()
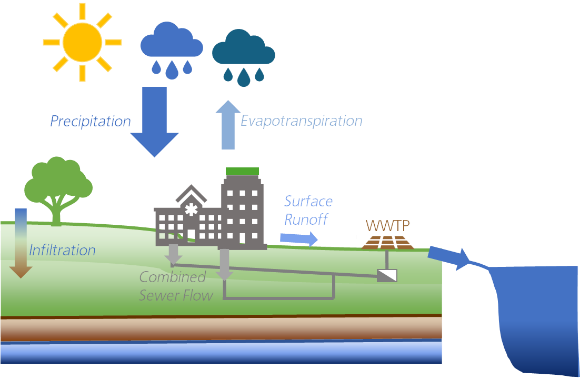
The natural water balance in urban areas is significantly influenced by infrastructure and a high degree of surface sealing. These factors can amplify the negative impacts of climate change, for example, through overheating in highly sealed city areas or the overloading of sewer systems during heavy rainfall events. Although numerous tools exist for modelling the water balance in rural or natural areas, a significant knowledge gap persists...(Download Read more (PDF, 96 KB))
Contact: Danielle Mayer ()

The recovery and reuse of resources from wastewater is facilitated by separating streams at the source. This includes separate collection of, for example, a urine and a fecal stream, a greywater stream, a rainwater stream. Each stream requires dedicated collection piping. In the case
of water reuse, the treated water requires distribution piping for indoor or
outdoor reuse. Replacing our current “one pipe in, one pipe out” paradigm with several parallel pipes increases. ... (Download Read more (PDF, 153 KB))
Contact: Rosanne Wielemaker ()